Five Seas, One Port: Moscow’s Global Link
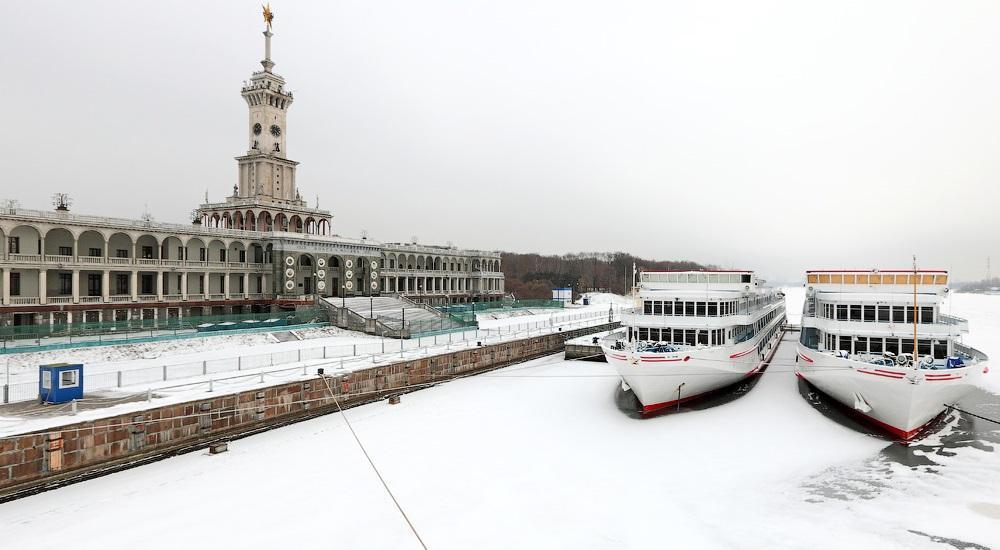
The Moscow Port of Five Seas, also known as the “Moscow Sea Port,” stands as a remarkable testament to Russia’s strategic ambitions in maritime trade and logistics. Located far from the traditional maritime gateways, Moscow’s port system is linked to five seas — the Baltic, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the White Sea, and the Sea of Azov. This integrated transport network provides a unique and multifaceted role for Russia, connecting inland waterways with vast international maritime routes.
Historical Roots and Development
The development of Moscow’s port facilities traces back to the late 19th century when the city began its industrial rise. Initially, the port served as a crucial nexus for trade within the Russian Empire. However, after the Soviet era, the importance of the port surged with the advent of modern transportation technologies, including the expansion of canals and the construction of sophisticated terminals that linked Moscow to the broader global economy.
The concept of a “port of five seas” was formalized under the Soviet Union in the mid-20th century, as Russia aimed to connect its vast inland waterway network to global maritime routes, boosting trade access to Europe, Asia, and the Middle East The project leveraged Russia’s vast network of rivers and canals, which allowed cargo to be transported from Moscow to far-reaching maritime ports. This not only reduced Russia’s dependence on external maritime infrastructure but also redefined its geopolitical positioning.
Strategic Position and Infrastructure
The Moscow Port of Five Seas draws its unique name from its connection to five significant bodies of water, each with its own geopolitical and economic importance:
- The Baltic Sea – The port offers access to the vital trade routes of Northern Europe, connecting Moscow to key maritime hubs such as St. Petersburg. This provides Russia with access to European markets, as well as the wider global network through the Northern Sea Route.
- The Black Sea – Linked through the Volga-Don Canal, the Moscow Port provides access to international shipping routes in the south, enabling trade with Mediterranean countries and beyond. Its proximity to the Bosporus Strait facilitates the flow of goods to and from global markets.
- The Caspian Sea – Through the Volga River, Moscow has an inland access point to the Caspian Sea, offering trade opportunities with Central Asia and Iran, and positioning Moscow as a potential logistical hub for these landlocked regions.
- The White Sea – The White Sea route connects to the Arctic, making Moscow’s port crucial for trade in the northern regions of Russia and beyond. The expanding interest in Arctic shipping only enhances its strategic importance.
- The Sea of Azov – Moscow’s port has access to this inland sea, providing a direct link to the southern shipping routes through the Kerch Strait, connecting the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov, with vital implications for trade with Turkey and the Mediterranean.
These five seas represent Russia’s ambitious plan to capitalize on its unique geographic positioning, where the country’s vast river systems serve as extensions of the global sea routes. The network of canals and rivers like the Volga, Don, and others forms an integrated whole that allows for a seamless flow of goods between Moscow and these five maritime gateways.
Economic Significance
The Moscow Port of Five Seas plays a key role in Russia’s economy, both as a trade hub and as a logistical facilitator for industries throughout the nation. The integration of inland waterways with international maritime routes has led to reduced shipping costs for goods moving to and from Russia’s heartland, including commodities like oil, gas, metals, and agricultural products. This has bolstered Moscow’s economic status, allowing it to serve as a distribution center for both raw materials and finished products.
Moreover, the port enhances Russia’s competitive edge in global trade. As an inland port, it allows goods to be transported via waterways, which is more economical than relying solely on rail or road transport. This makes it an attractive option for trade with countries that would otherwise face prohibitive shipping costs or time constraints due to geographical barriers.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its advantages, the Moscow Port of Five Seas faces a number of challenges that could limit its full potential. One of the primary issues is the age of the infrastructure. Many of the canals and river routes connecting Moscow to the seas are in need of modernization to handle the demands of 21st-century shipping. Additionally, while the waterways allow for larger cargo movements, they cannot compete with the efficiency and scale of more established ports, such as those in St. Petersburg or Novorossiysk.
The geopolitical landscape also adds complexity to the future of the port. Regional tensions, particularly in the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, could affect the stability of the shipping routes passing through these waters. Moreover, international sanctions, trade policies, and environmental concerns about waterway usage could impact the port’s viability in the long term.
Nevertheless, Moscow’s position as a nexus between Europe, Central Asia, and the Arctic makes it a highly strategic asset in Russia’s pursuit of greater economic and geopolitical influence. Plans to upgrade infrastructure, improve connectivity with other Russian ports, and enhance navigability through the various canals are already in progress. These developments, coupled with the increasing global interest in the Arctic and Eastern Europe, bode well for the continued growth and importance of the Moscow Port of Five Seas.
Final Analysis
The Moscow Port of Five Seas stands as a symbol of Russia’s long-term vision to assert itself as a formidable force in global trade and geopolitics. Its geographical uniqueness, linking five seas through a network of rivers and canals, makes it a key player in the transport and logistics sectors. As Russia continues to modernize its infrastructure and expand its international influence, the Moscow Port of Five Seas will likely play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of Eurasian trade. The port is not just a transportation hub but also a strategic asset that reinforces Russia’s ambitions to connect its heartland with global maritime routes and markets, ensuring its place at the crossroads of global commerce.
Despite these challenges of Ukraine conflict, Russia has been working to maintain trade through alternative routes, including strengthening connections with Asian markets, utilizing its internal river and canal systems, and enhancing cooperation with countries that have not imposed sanctions. However, the overall volume of trade through Moscow’s ports has been reduced, and its long-term prospects remain uncertain amid the ongoing conflict.
Why These 7 Little-Known Facts About Internet Privacy Are Crucial for Your Safety | Maya




I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.