Rotterdam and the Rhine River: A Geographical and Economic Nexus
Rotterdam, located in the western Netherlands, is a city that has come to symbolize modernity and industrial might. It is closely tied to the Rhine River system, which has played a central role in shaping the geography, economy, and culture of the city. Though Rotterdam itself is not directly on the main course of the Rhine, it is situated at the river’s mouth, making it a crucial gateway between Europe’s inland and the North Sea. The Rhine’s influence on Rotterdam is profound, making the city a vital hub in European commerce, transportation, and history.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Geographic Context
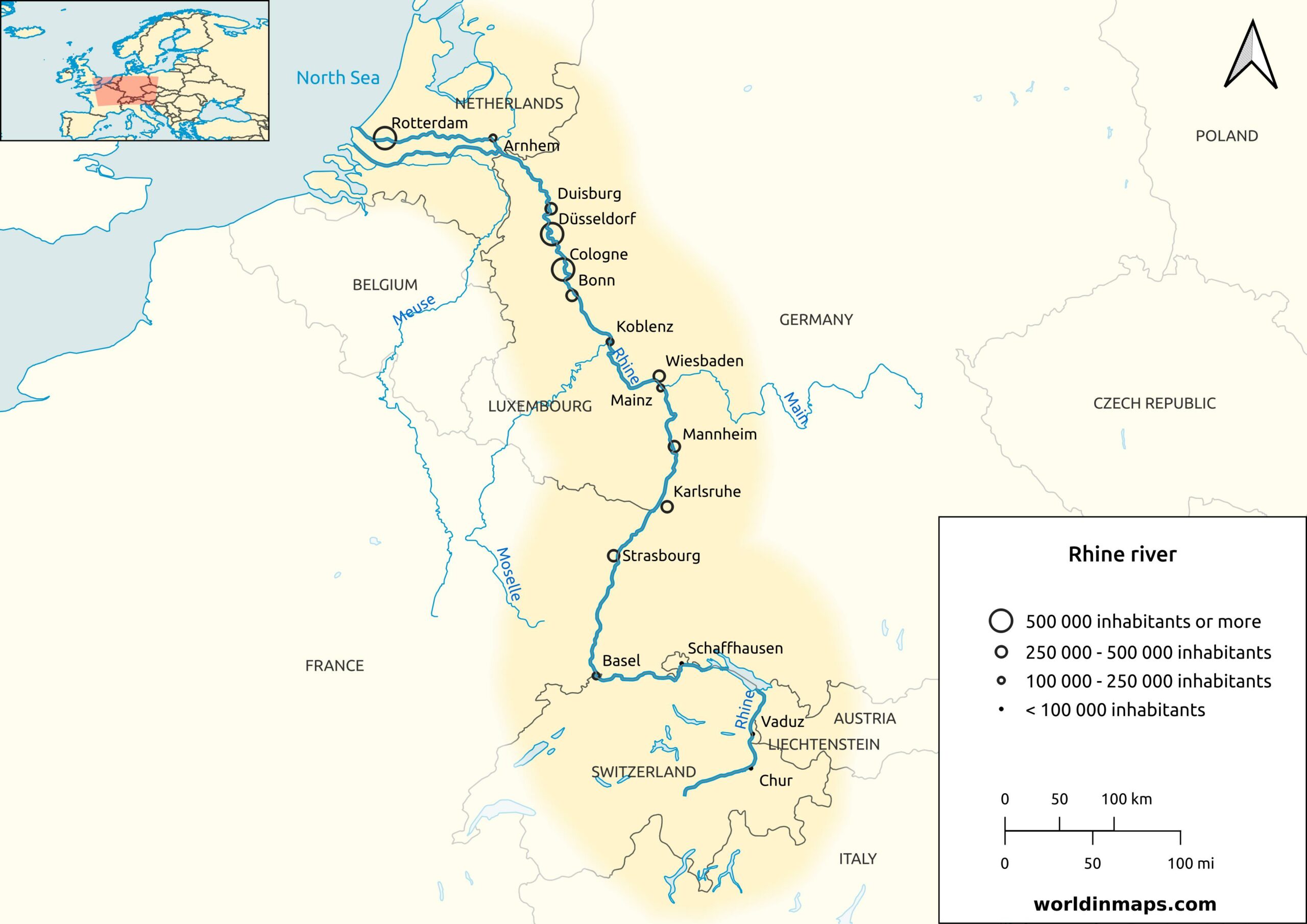
The Rhine River originates in the Swiss Alps, flowing northward through Switzerland, Germany, and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea. Stretching over 1,230 kilometers, it ranks among the most vital waterways in Europe. The river’s course has been pivotal in shaping the physical and economic landscapes of the regions it traverses. While the river cuts through multiple countries, Rotterdam is particularly significant due to its position at the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta, where the Rhine splits into several branches before emptying into the North Sea.
Rotterdam lies at the mouth of the Rhine, where it converges with the Meuse and Scheldt rivers, a location that has historically made it a vital port. The city itself is not located directly on the Rhine’s primary course but rather on one of its branches, the Waal River, which flows into the North Sea through the port of Rotterdam. This strategic location has made Rotterdam one of the busiest and most important port cities in the world, directly benefiting from the river’s extensive transportation network.
Historical and Economic Significance
The history of Rotterdam is closely intertwined with its riverine geography. Initially founded as a small fishing village in the 13th century, the city’s fortunes have always been closely linked to its access to water. However, the devastation of Rotterdam during World War II marked a turning point in its history. On May 14, 1940, the city was bombed by the German Luftwaffe, leading to the destruction of much of its infrastructure, including historical buildings. After the war, Rotterdam embraced modernist architecture in its reconstruction, emphasizing functionality and innovation. This shift not only marked a physical transformation of the city but also its rise as an industrial powerhouse.
Rotterdam’s proximity to the Rhine has been a defining factor in its economic success. The Port of Rotterdam, Europe’s largest and the world’s busiest outside of Asia, serves as a critical gateway for goods moving between inland Europe and the global market. The port’s direct connection to the Rhine River allows it to facilitate the movement of goods deep into the heart of Europe. The river connects Rotterdam to major European industrial regions, including Germany’s Ruhr Valley and the Swiss and French borders, creating a seamless trade route for goods ranging from industrial products to raw materials.
The Rhine’s influence on Rotterdam extends beyond shipping. The port is a hub for industries such as petrochemicals, logistics, steel production, and container transport, all of which rely heavily on the river for the movement of raw materials and finished goods. The city’s modern economy has been built around the river’s infrastructure, and Rotterdam has leveraged its position as a global trading center.
Rotterdam’s Role in European Trade and Transport
The strategic location of Rotterdam, at the mouth of the Rhine, establishes it as a crucial point for Europe’s inland waterways. The Rhine-Main-Danube Canal system connects the Rhine to the Danube River, allowing goods to be transported from the North Sea deep into the heart of Europe, reaching as far as the Black Sea. This connectivity has cemented Rotterdam’s position as Europe’s primary logistics and transport hub. Its access to the Rhine also makes Rotterdam an essential link in the European economic supply chain.
The river is a key player in Rotterdam’s position as a hub for global trade. It serves as a conduit for the movement of millions of tons of goods, ranging from bulk items like coal, oil, and chemicals to high-value consumer goods. Rotterdam’s port is a key node in the transshipment of goods to and from other parts of the world. Its status as a primary hub for container traffic means that products from Asia, Africa, and the Americas are often transferred here before continuing their journey to the rest of Europe.
Several cities are located near or along the Rhine River, which flows through Switzerland, Germany, France, and the Netherlands. Here’s a brief list of notable cities near the Rhine:
- Basel (Switzerland) – Basel, found at the meeting point of Switzerland, France, and Germany, lies on the banks of the Rhine.
- Strasbourg (France) – Strasbourg sits on the western bank of the Rhine in northeastern France, near the border with Germany.
- Cologne (Germany) – In the heart of western Germany, Cologne is one of the largest cities, sitting directly on the Rhine River.
- Düsseldorf (Germany) – On the eastern bank of the Rhine, Düsseldorf is a major city in western Germany.
- Bonn (Germany) – A former capital of West Germany, situated along the river in western Germany.
- Mainz (Germany) – At the confluence of the Rhine and Main rivers in western Germany, you’ll find the city of Mainz.
- Koblenz (Germany) – Koblenz is a historic city located where the Moselle River flows into the Rhine.
- Rotterdam (Netherlands) –Rotterdam is positioned near where the Rhine meets the North Sea, in the Netherlands.
- Leverkusen (Germany) – Leverkusen, a city near Cologne, is positioned along the Rhine River.
These cities have rich histories and cultural significance due to their location along the Rhine.
Modern Challenges and Sustainability
Despite its success, Rotterdam faces significant challenges related to its geographical location. Due to climate change, the city’s port is at risk from rising sea levels, compounded by the constant need for infrastructure maintenance.To address these issues, the city has invested heavily in sustainability initiatives. Rotterdam is known for its focus on green technologies, renewable energy, and environmental innovation, seeking to create a more sustainable future for its port and industries. The city is also active in flood protection measures, utilizing its extensive knowledge of water management and engineering to protect both the city and its vital port.
Hormones and Health: The Key Players Behind Your Body’s Functions | Maya
In summary
Rotterdam’s connection to the Rhine River has shaped the city into a global economic powerhouse. The river has provided the city with access to international trade routes, enabling it to become one of the most important ports in the world. From its origins as a small fishing village to its modern incarnation as a symbol of industrial strength and innovation, Rotterdam’s geographic position at the mouth of the Rhine has been integral to its success. In the 21st century, the city continues to build on its riverine legacy, balancing the demands of global commerce with sustainability efforts. The Rhine, with its complex system of waterways, remains a central force in Rotterdam’s ongoing development, ensuring that the city will continue to play a crucial role in Europe’s economic landscape.
AC and DC Power: Why Do We Need Both to Power Our World? | Maya