The Hidden Potential of GLP-1 Drugs You Haven’t Heard About: If you’ve followed health news lately, you’ve probably heard about GLP-1 drugs — medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro that have become household names.
At first, they were celebrated as game-changers for type 2 diabetes. Then came the second wave: dramatic weight-loss results, sparking global demand and headlines everywhere.
But the story doesn’t end there. Scientists are now uncovering new, surprising benefits of GLP-1 drugs — from improving heart health to protecting the brain, and even potentially treating addiction.
Let’s explore how these medications are evolving from metabolic helpers to multi-system health boosters.
What Exactly Are GLP-1 Drugs?
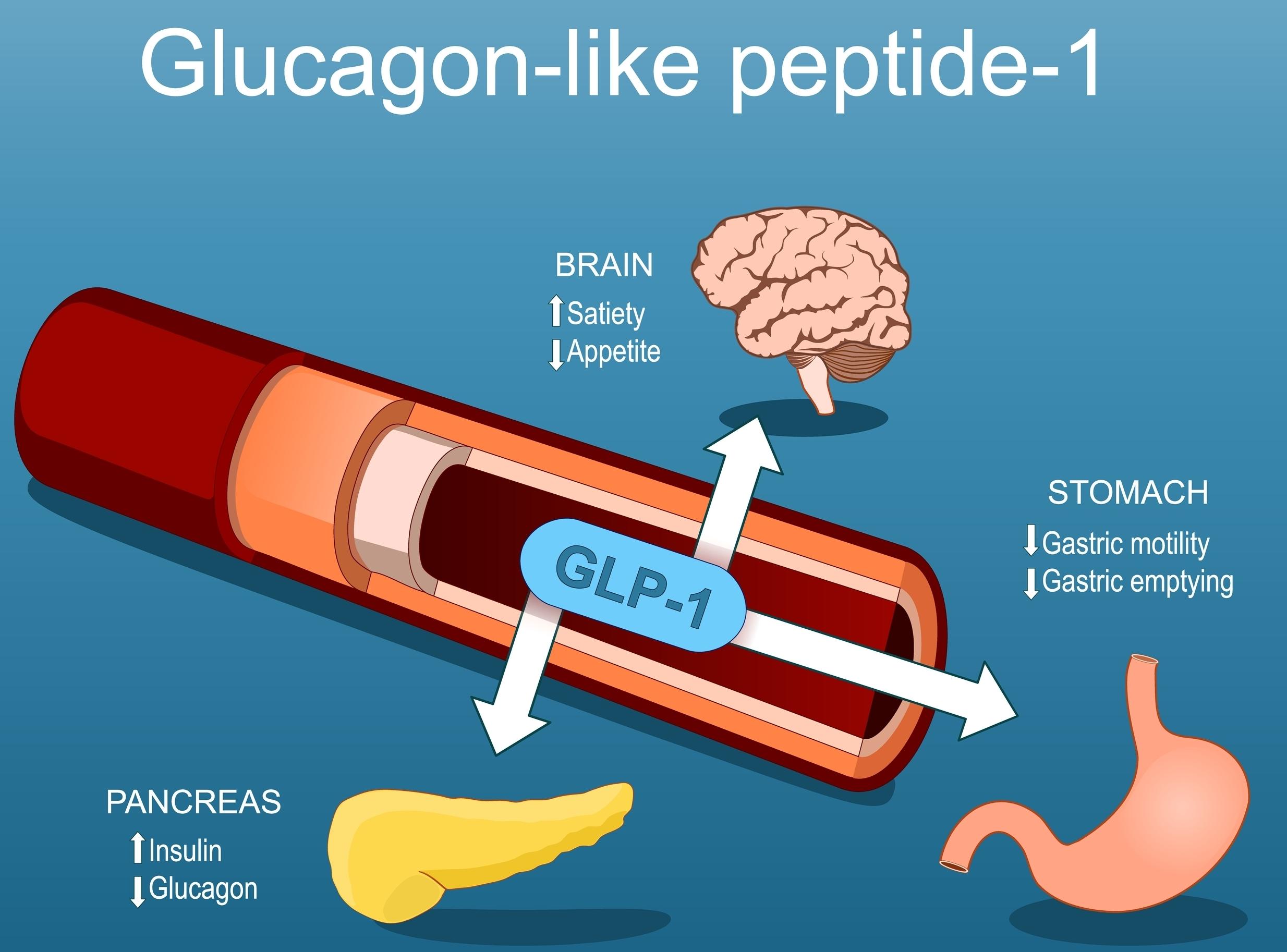
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, a natural hormone produced in your gut.
After you eat, GLP-1 helps:
-
Trigger insulin release, lowering blood sugar
-
Slow down digestion, so you feel fuller for longer
-
Reduce appetite and cravings
-
Support heart and metabolic function
GLP-1 medications mimic this natural hormone. The first versions were approved in the early 2000s to help people with type 2 diabetes control blood glucose levels.
Then doctors noticed something fascinating — patients were losing significant weight, even without major diet changes. That discovery led to new formulations like semaglutide (Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro) specifically for weight management.
Now, with millions using these drugs worldwide, researchers are asking: What else can they do?
Why Are Scientists So Interested in GLP-1 Beyond Metabolism?
Because GLP-1 receptors aren’t only in the pancreas and gut — they’re found throughout the body, including the heart, brain, kidneys, and immune system.
That means these drugs can potentially influence a wide range of biological processes, not just blood sugar.
In recent years, studies have started linking GLP-1 treatments to improvements in:
-
Heart health
-
Cognitive function
-
Inflammation control
-
Addiction and mental health regulation
-
Liver protection
The list keeps growing as scientists uncover new pathways.
1. Heart Health: A Clear Win
One of the most exciting findings is that GLP-1 drugs seem to protect the heart — even in people without diabetes.
Large clinical trials have shown that drugs like liraglutide and semaglutide can:
-
Reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke
-
Lower blood pressure
-
Improve cholesterol profiles
-
Support healthy blood vessel function
In 2023, the SELECT trial made headlines when it showed that semaglutide reduced the risk of major cardiovascular events in overweight individuals without diabetes.
This was the first solid evidence that GLP-1 drugs offer heart protection beyond glucose control.
Cardiologists are now calling it “one of the most important breakthroughs in preventive medicine.”
2. Brain Health and Alzheimer’s Disease
Here’s where things get even more fascinating.
GLP-1 receptors are abundant in the brain, especially in regions tied to learning, memory, and emotion. Animal studies suggest GLP-1 drugs may:
-
Reduce inflammation in brain tissue
-
Protect neurons from degeneration
-
Improve insulin signaling in the brain (which supports memory and cognition)
Several early-stage trials are testing GLP-1 drugs for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Results so far hint at slowed cognitive decline and better brain metabolism.
If these benefits hold up in larger studies, GLP-1 medications could become the first metabolic drugs to also shield the brain from aging.
3. Addiction and Mental Health
Could the same drug that curbs sugar cravings also reduce cravings for alcohol or nicotine?
Early research says — possibly yes.
GLP-1 acts on reward centers in the brain, influencing dopamine pathways linked to motivation and pleasure. That’s why researchers are testing GLP-1 agonists for:
-
Alcohol use disorder
-
Nicotine addiction
-
Binge eating disorder
Preliminary studies show that people taking semaglutide report less interest in alcohol and reduced impulse behaviors.
Scientists suspect GLP-1 drugs might help “rebalance” how the brain experiences reward — offering a potential new route for treating addiction.
Some users have even reported less anxiety and improved mood stability, though formal studies are still underway to confirm these effects.
4. Fatty Liver Disease and Inflammation
Another promising area is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a growing epidemic driven by poor diet and obesity.
GLP-1 drugs help reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower inflammatory markers.
Trials are showing potential reversal of NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) — a more serious liver condition that can lead to cirrhosis.
Because inflammation plays a role in many chronic diseases, GLP-1 drugs’ anti-inflammatory properties may also benefit conditions like arthritis, kidney disease, and even some autoimmune disorders.
5. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Fertility
Women with PCOS often struggle with insulin resistance and weight gain — both areas where GLP-1 drugs excel.
Recent studies show that these medications can:
-
Improve insulin sensitivity
-
Promote healthy ovulation
-
Reduce androgen levels
-
Support weight management for fertility outcomes
Doctors are cautiously optimistic that GLP-1 drugs could become a valuable tool in PCOS management and reproductive health — though more data is needed before they become a standard therapy.
How Do GLP-1 Drugs Do All This?
The magic lies in how GLP-1 interacts with multiple systems.
It’s not just a metabolic regulator — it’s a full-body communicator.
Here’s what happens:
-
It sends signals to the brain that control hunger, emotion, and motivation.
-
It improves blood vessel elasticity and reduces inflammation in the heart.
-
It enhances cell energy use, lowering fat accumulation in the liver.
-
It regulates insulin and glucagon, balancing blood sugar and energy flow.
In essence, GLP-1 drugs “reset” the body’s metabolic communication network — making them one of the most versatile classes of modern medicine.
Challenges and Cautions
Of course, no medication is without limits. GLP-1 drugs can cause:
-
Nausea or digestive discomfort (especially in early weeks)
-
Rare risks like pancreatitis or gallbladder issues
-
Nutrient deficiencies if food intake becomes too low
And the long-term safety of using these drugs for non-diabetic conditions still needs further study.
Doctors emphasize that lifestyle changes — balanced nutrition, exercise, and mental health care — remain essential, even alongside GLP-1 therapy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are GLP-1 drugs safe for people without diabetes?
Generally yes, under medical supervision. Clinical trials like SELECT showed benefits in non-diabetic individuals, but dosing and monitoring are crucial.
2. Can they really help with addiction?
Early results are promising but not conclusive. Research is ongoing to confirm how GLP-1 affects reward pathways in the brain.
3. Will these drugs become standard for heart health or brain protection?
Possibly. Cardiologists and neurologists are closely watching the data. If benefits continue to hold, guidelines may expand in the next few years.
4. Are all GLP-1 drugs the same?
No. Each varies in structure, duration, and potency. Semaglutide and tirzepatide are among the most effective for weight and metabolic benefits.
5. Should I take GLP-1 drugs for general health?
Not yet. These are prescription medications meant for specific conditions. Always consult a healthcare provider — never self-prescribe based on trends.
The Bottom Line
GLP-1 drugs are no longer just “diabetes medications.”
They’re emerging as multi-purpose therapies that may protect the heart, brain, liver, and even mental health.
As science continues to uncover their broader impact, these drugs could redefine how we treat chronic disease and emotional well-being — not through one system at a time, but through the whole-body connection.
The era of metabolic medicine has officially arrived — and GLP-1 drugs are leading the way.